Everything about 10-Meter Radio

Everything about 10-Meter Radio
The 10-meter band, is amateur radio one of the most popular radio bands. But what is a 10-meter radio, like Retevis HS4,and how is it different from other radio bands? In this blog, we will discuss everything you need to know about the 10-meter radio.
1. What is a 10-meter radio?
The 10-meter radio is a type of amateur radio that operates on the 28 MHz frequency band. It is a high-frequency radio band that allows for long-distance communication, making it popular among amateur radio operators who want to talk to people from other parts of the world.
2. What's a 10-meter used for?
The 10-meter radio is mainly used for two-way communication between amateur radio operators. It is used for various purposes, including talking to people in other countries, participating in contests, emergency communication, and experimentation with different modes and equipment.
Talk to other amateur radio operators: One of the main reasons people get into amateur radio is to make contacts with other operators around the world. With a 10-meter radio, you can communicate with other operators using various modes such as SSB, AM, and FM.
Participate in contests: Amateur radio contests are a fun and competitive way to test your skills and make contacts. There are several contests throughout the year that focus on the 10-meter band.
Experiment with antennas: Antennas are a critical part of any radio system, and experimenting with different types of antennas can help you optimize your setup for better performance. With a 10-meter radio, you can try out different antennas and see how they affect your signal.
Explore digital modes: With the right equipment and software, you can use your 10-meter radio to operate in various digital modes such as PSK31, RTTY, FT8, and JT65.
Help with emergency communications: In times of emergency, amateur radio operators can be called upon to provide critical communication services. With a 10-meter radio, you can be part of a local or regional emergency communications network.
DXing: DXing is the art of making long-distance contacts with other operators around the world. With a 10-meter radio, you can try to make contacts with stations in other countries and earn awards for your achievements.
Experiment with different power levels: 10-meter radios usually have adjustable power output levels ranging from 1 to 100 watts. Experimenting with different power levels can help you understand how they affect your signal and reception.
3. Do I need a license to operate it and are there any privileges and restrictions for each class?
Yes, you need a license to operate a 10-meter radio. The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) regulates the use of radio frequencies in the United States, and you need to pass an exam to obtain a license. There are three levels of licenses: Technician, General, and Extra. The Technician license allows you to operate on the 10-meter band, while the General and Extra licenses allow you to operate on other frequencies as well.
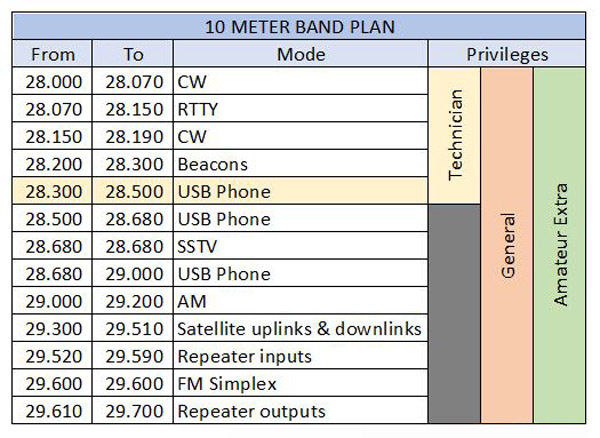
Technician Class License:Technician class license holders have operating privileges on the 10-meter band from 28.000 MHz to 28.500 MHz. They are permitted to operate on all modes of transmission that are legal for amateur radio operators, including voice, digital, and CW (Morse Code). However, they are limited to 200 watts PEP output power.
General Class License:
General class license holders have expanded operating privileges on the 10-meter band, with access to the full band from 28.000 MHz to 29.700 MHz. They have the same operating mode privileges as Technician class license holders, but with a higher power limit of 1500 watts PEP.
Extra Class License:
Extra class license holders have the highest operating privileges on the 10-meter band, with the same privileges as General class license holders. They also have the highest power limit of 1500 watts PEP.
It's important to note that these operating privileges are specific to the 10-meter band and may differ on other amateur radio bands. It's also important to be aware of any frequency allocations, band plans, and operating protocols that may be in effect on the 10-meter band or in a particular operating region.
Amateur radio operators should always operate within their license privileges and comply with all regulations and guidelines set forth by the FCC and other governing bodies.
There are no operating modes that are specifically reserved for a particular license class on the 10-meter band in the United States. All licensed amateur radio operators are authorized to use any operating mode on the 10-meter band, including voice, digital modes, and CW (Morse code).
However, it's worth noting that some digital modes may require higher power levels than what is allowed for lower-class licenses. For example, the JT65 and JT9 digital modes may require up to 1500 watts of power for reliable operation, which is only allowed for Extra class license holders. So while all license classes are technically allowed to use these modes, they may not be practical or effective without the appropriate license and equipment.
In general, the operating mode that a user chooses to use on the 10-meter band will depend on their personal preferences and equipment capabilities. Some popular modes on the 10-meter band include SSB (single sideband), FM (frequency modulation), and various digital modes such as FT8 and PSK31.
4. How far will a 10-meter radio transmit?
The range of the 10-meter band can vary depending on a number of factors, including the type of antenna used, the power output of the radio, the mode of transmission, and the conditions of the ionosphere.
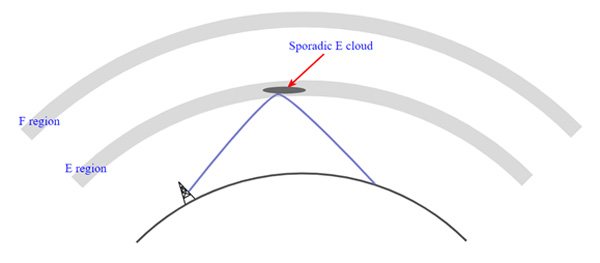
Under normal conditions, the 10-meter band can typically support communications over distances of several hundred miles (or kilometers) using SSB voice or digital modes such as RTTY or PSK31. With good propagation conditions, such as during peak solar activity periods or during Sporadic E propagation events, communication distances of over a thousand miles (or kilometers) can be achieved on the 10-meter band.
Ultimately, the range of the 10-meter band is highly dependent on a variety of factors, and can vary widely from one situation to another. Amateur radio operators should always use good operating practices, make responsible use of their equipment, and operate within the limits of their license and local regulations.
5. What's the most popular mode for a 10-meter radio?
A 10-meter radio supports several modes of operation, including SSB (Single Side Band), CW (Continuous Wave), AM (Amplitude Modulation), FM (Frequency Modulation), and digital modes such as RTTY (Radio Teletype), PSK31 (Phase Shift Keying), and FT8 (Franke-Taylor design, 8-FSK modulation).
The most popular mode for a 10-meter radio is Single Sideband (SSB). SSB is a voice mode that allows for clear, high-quality communication over long distances. Unlike AM, which is the other common voice mode used on 10-meter radios, SSB provides more power efficiency and better audio quality. This makes it ideal for long-range communication, especially in challenging conditions where signals may be weak or prone to interference.
Another reason why SSB is popular on 10-meter radios is that it allows for a wider range of frequencies to be used within the 10-meter band. SSB signals can be tuned to occupy just a few kilohertz of bandwidth, allowing multiple SSB signals to occupy the same frequency range without interfering with each other.
In addition to SSB, other modes that are popular on 10-meter radios include FM, CW (Morse code), and digital modes such as PSK31 and FT8. Each mode has its own strengths and weaknesses, and choosing the right mode for a particular situation depends on factors such as the distance between stations, the available equipment, and the operator's preferences and skills.

6. What's the difference between 10-meter radios and CB radios?
While 10-meter radios and CB (Citizens Band) radios (like Retevis HS4) may look similar, they are designed for different purposes and operate on different frequency bands. Actually 10-meter radios are not designed to communicate with CB Radios. Here are some key differences between 10-meter radios and CB radios:
Frequency range: CB radios operate on a narrow band of frequencies between 26.965 MHz and 27.405 MHz. In contrast, 10-meter radios operate on a wider band of frequencies between 28.000 MHz and 29.700 MHz.
Power output: CB radios are limited to a maximum power output of 4 watts for AM and 12 watts for SSB, while 10-meter radios can output up to 200 watts of power (for Novice and Technician classes).
Licensing requirements: In most countries, CB radios can be used without a license, while operating a 10-meter radio requires a valid amateur radio license.
Modes: CB radios are limited to AM and SSB modes (and the newly added FM), while 10-meter radios can operate in a wider range of modes, including FM, CW, and digital modes.
Antenna requirements: 10-meter radios have a shorter antenna length. CB radio antennas are a bit longer. Without considering other parameters a quarter wave antenna for 10m is 2.50 meters long and for CB the same quarter wave antenna is 2.75m long. Both of them must be tuned with an SWR meter and have its SWR set for the closest ratio to 1:1 as possible to work properly.
Range: Due to their limited power output, CB radios have a shorter range than 10-meter radios. 10-meter radios can make longer-distance contacts, especially when using SSB mode and a high-gain directional antenna.
Use cases: CB radios are commonly used for short-range communications between vehicles, while 10-meter radios are primarily used by amateur radio operators for long-distance communication and experimentation.
7. What Antenna should a 10-meter radio use?
The type of antenna you use with a 10-meter radio will depend on the mode of operation and the location of the antenna. For general use, a vertical or dipole antenna is suitable for a 10-meter radio. A beam antenna is also an option for those looking for directional capabilities.
8.The Antenna
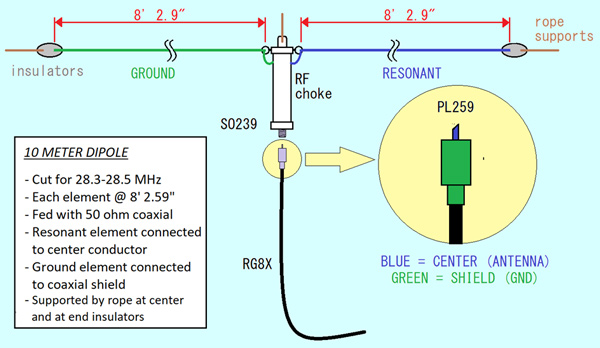
Of course you will need a resonant antenna in order to put your signal out on 10 meters, and the easiest and most inexpensive way to do this is to construct a classic half wave wire dipole antenna. Building your own 10 meter dipole is simple, easy, affordable and fun.
The dipole is a straight electrical conductor consisting of two equal lengths of #12 or #14 stranded wire with a combined length measuring 1/2 wavelength from end to end. It is supported with rope or nylon cored from the center and each end and connected at the center to a radio-frequency (RF) feed line that is then connected to your transceiver.
A half wave dipole cut and tuned for the center frequency of 28.400mhz should cover all of the Technician 200khz spread with low SWR and will allow you to work the entire sub-band without the need of a tuner.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the 10-meter band offers a unique and exciting opportunity for amateur radio operators to communicate over a range of distances using a variety of modes and frequencies. Whether you're interested in voice communication, digital modes, or CW, the 10-meter band has something to offer for operators of all license classes. Its versatility and accessibility make it one of the most appealing bands in the amateur radio spectrum.







